Get Started
Hyperlane can be deployed by anyone to any chain. This guide covers sending your first interchain message from a new EVM chain. If you'd like to deploy to a Cosmos appchain, follow this community-submitted guide.
By the end of this guide you will have deployed and configured your Mailbox smart contract and off-chain agents, allowing developers to send interchain messages to and from your chain.
This guide has been specifically made to demonstrate how to connect a chain that already has Hyperlane on it to a new chain that does not have Hyperlane.
Terminology
The "local chain" is your new chain that you want to deploy Hyperlane onto.
A "remote chain" is a chain with an existing Hyperlane deployment that you want your local chain to send & receive messages to & from.
Overview
There are five steps in this guide:
- Set up keys that you will use to deploy contracts and run validators and relayer.
- Deploy contracts to the local chain and to every remote chain with which the local chain will be able to send and receive messages.
- Run validators and relayer using Kurtosis. Validators provide the signatures needed for the Interchain Security Modules you deployed in step 2. The relayer will deliver messages between chains you deployed contracts to.
- Send a test message to confirm that your relayer is able to deliver messages to and from each pair of chains
- Deploy a warp route to send token value, not just messages, across chains
Getting Started
1. Set up keys
There are three keys you must set up and fund.
To get started, you can simplify by using the same hexadecimal key for all three roles.
| Key Role | Description | Funding Needs |
|---|---|---|
| Contract Deployer | 32 byte hexadecimal private key | Funded on all the chains on which we need to deploy contracts. |
| Validator Accounts | A list of validator addresses that will sign outbound messages from your local chain. Just one validator works to get started quickly. | A small amount so validators can announce the location of their signatures onchain with a one-time transaction |
| Relayer Accounts | The single relayer you will operate requires an account on each chain it will deliver messages to & from | The relayer must have a balance on all chains it's relaying between. |
For instructions on how to generate keys, see the agent keys section. Your deployer key must be a hexadecimal key, while validator and relayer keys can be hexadecimal or AWS KMS.
If deploying on a local network using Foundry's Anvil, use the following command to fund your newly-generated account. It uses one of the pre-funded private keys to transfer 1 ETH to the address in the $YOUR_TARGET_ADDRESS environment variable.
cast send $YOUR_TARGET_ADDRESS \
--private-key 0xac0974bec39a17e36ba4a6b4d238ff944bacb478cbed5efcae784d7bf4f2ff80 \
--value $(cast tw 1)
2. Deploy contracts
Once you have set up deployer, validator, and relayer keys it's time to use the Hyperlane CLI to deploy smart contracts to the local and remote chains.
On the local chain, we will deploy:
- The core contracts, including a Mailbox that can be used to send and receive messages.
On all chains, we will deploy:
- A Multisig ISM that can be used to verify inbound messages from the other local & remote chains.
- An
InterchainGasPaymaster, which can be used to pay our relayer for delivering interchain messages. - A
TestRecipient, which we will send messages to, in order to test that everything is working correctly.
Setup
First, install the Hyperlane CLI.
npm install -g @hyperlane-xyz/cli
Chains
The deployment will require basic information about any chains it will be interacting with. If the target chains are not already in the Hyperlane Registry, you must specify chain metadata for them. See the CLI reference for details.
To see what chains are in the currently known, run the following command:
hyperlane chains list
To create a chain metadata config for any other chains, run the following command:
hyperlane config create chain
Or you can define the config manually. See the ChainMetadata type for its schema. See chain-config.yaml for an example.
ISM
Now the CLI will know how to interact with all your chains, but it will also need to know how to configure your Interchain Security Module (ISM).
To create a multisig ISM configs, you can define it manually using JSON or YAML (see example config here), or create it with the following command:
hyperlane config create ism
When asked about the multisig type, choose message id ism. In the context of this guide, we will be using a 1/1 multisig, so choose a threshold of 1 and enter the address of your key.
Dry Run
Prior to executing a deployment, you can execute a dry-run via --dry-run <CHAIN_NAME> or -d <CHAIN_NAME> to ensure that the deployment will be successful as well as provide analytics on the gas costs of deployment. This will not execute any transactions but will simulate a deployment to display a list of required contracts and their respective gas costs.
In addition to validating your upcoming deployment, you can provide the address of the EOA you intend to deploy with via --key or -k.
This will ensure you have approximately enough funds to complete the deployment, without providing access to your private key to pay for transactions.
In order to execute a dry-run, you will need an Anvil node running in a separate terminal instance.
To spin up an Anvil node, run anvil.
For more on Anvil and installation, checkout Foundry's Anvil docs.
hyperlane deploy core --dry-run chain1 \
--targets chain1 \ # one of the chains you want to bridge between
--ism $MULTISIG_CONFIG_FILE \ # path to ism.yaml config e.g. ./configs/ism.yaml
--key $YOUR_DEPLOYER_ADDRESS # (optional) your account address to be impersonated via Anvil; defaults to the HYP_KEY env variable
--registry # (optional) path to your primary registry; defaults to the Hyperlane github registry \
--overrides # (optional) path to a override registry; defaults to the local ./ path
Deploy
We're now ready to use the deploy core command to deploy the Hyperlane contracts. To pay for transactions, the command will need the contract deployer key from step 1, which can be provided via the HYP_KEY env variable or as a command argument.
hyperlane deploy core \
--targets chain1,chain2,... \ # all the chains you want to bridge between
--ism $MULTISIG_CONFIG_FILE \ # path to ism.yaml config e.g. ./configs/ism.yaml
--key $YOUR_DEPLOYER_PRIVATE_KEY # (optional) your private key to pay for transactions; can also be provided via HYP_KEY env variable
--registry # (optional) path to your primary registry; defaults to the Hyperlane github registry \
--overrides # (optional) path to a override registry; defaults to the local ./ path
Verify
Deployment contract artifacts will be written to the configured registries. By default, you'll find the new addresses in the local directory you ran the command from (e.g. ./chains/chain1/addresses.yaml).
The deployment will also generate a Hyperlane Agent config, which is written to ./configs/agent.json by default, but can be configured with the --agent flag.
3. Run validators and relayer
This section covers how to 1-click deploy agents using a third party. To run the Hyperlane agent binaries yourself, follow the Local Agents guide.
We've partnered with Kurtosis to provide a single-click validator and relayer deployment in the cloud. You'll receive a one-month trial during which your validator and relayer run in Kurtosis Cloud for free. After your trial ends, you'll need to either run your validator and relayer yourself or purchase a Kurtosis Cloud subscription.
To get started, use the deploy kurtosis-agents command to generate a link for configuring your Kurtosis deployment.
hyperlane deploy kurtosis-agents
Follow the prompts and then click on the Kurtosis Cloud link output by the command.
If this is your first time using Kurtosis Cloud, you'll need to sign in with Google and Kurtosis will provision a remote cloud instance for your validator and relayer in roughly 2 minutes.
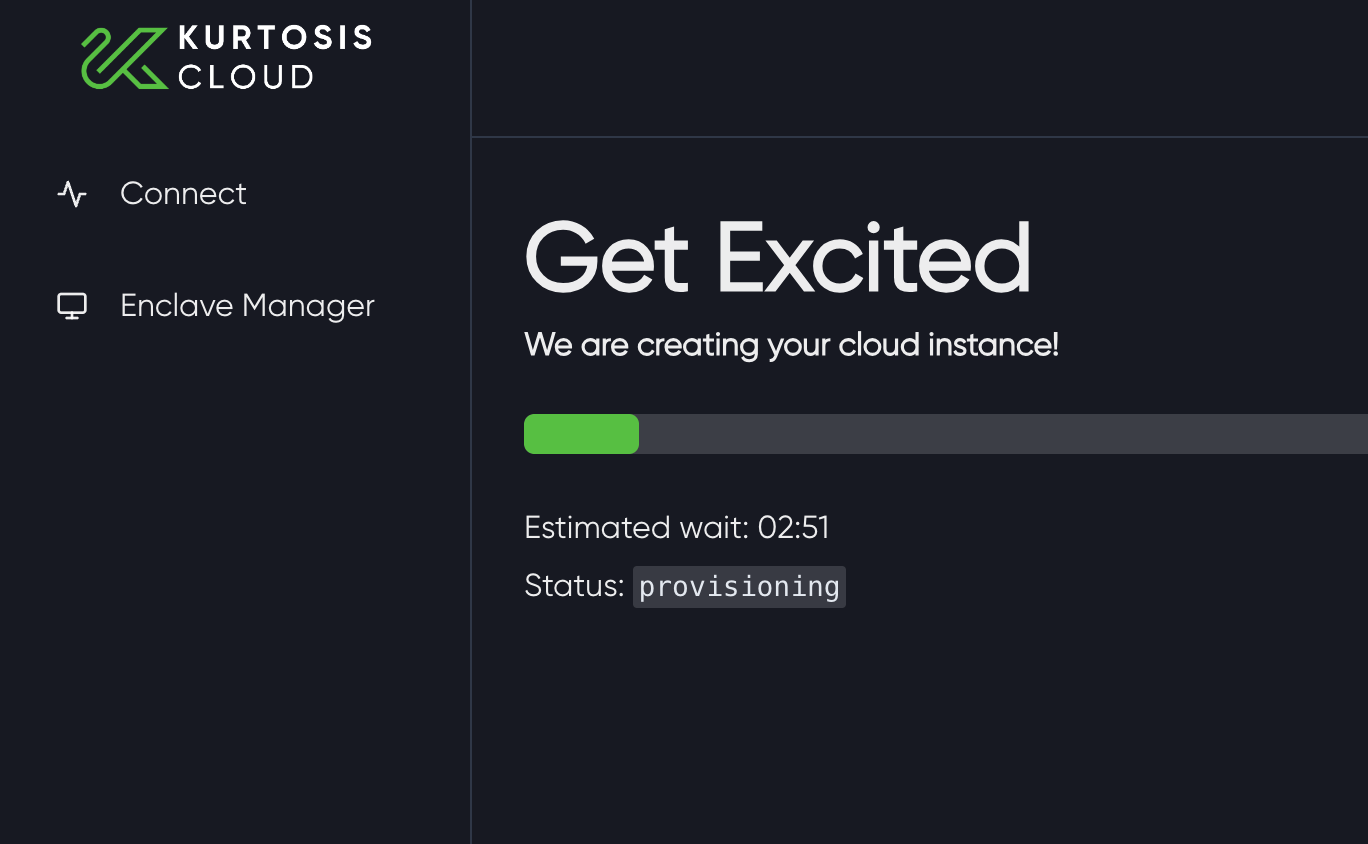
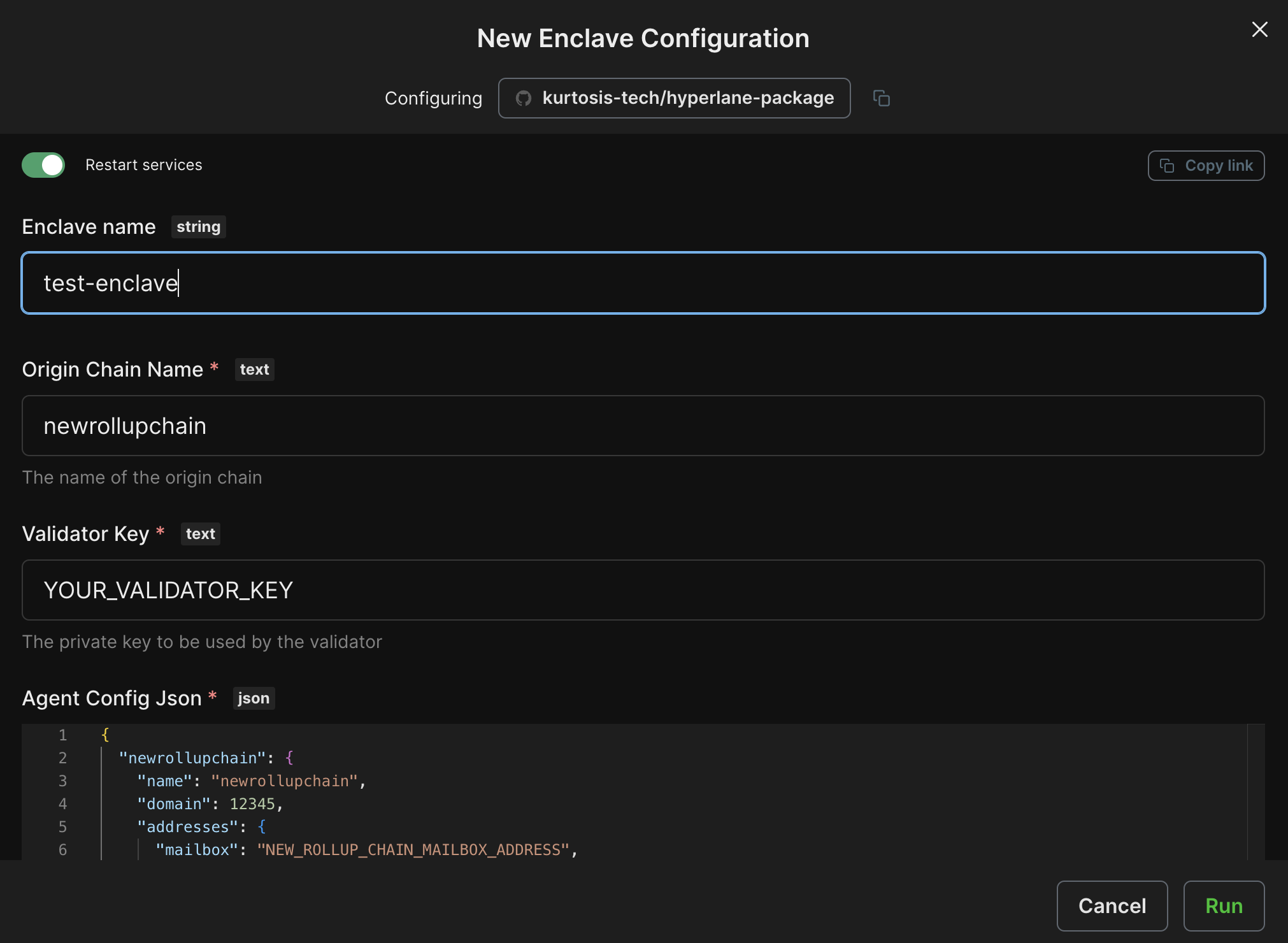
A prefilled configuration screen will pop up with all your relayer and validator information from Steps 1 and 2.
If you are having issues deploying agents on Kurtosis Cloud through the CLI, you can manually enter this information by:
- Signing into Kurtosis Cloud.
- Clicking
Runon the Hyperlane Package. - Filling in the configuration modal.
The last step will be to input your Validator Key from Step 2. The screenshots below show an example prefilled configuration.
The Kurtosis team is still building the secrets functionality of Kurtosis Cloud, so for now do not enter any sensitive information (e.g. your private keys) into Kurtosis! Only testing and non-sensitive values should be used.
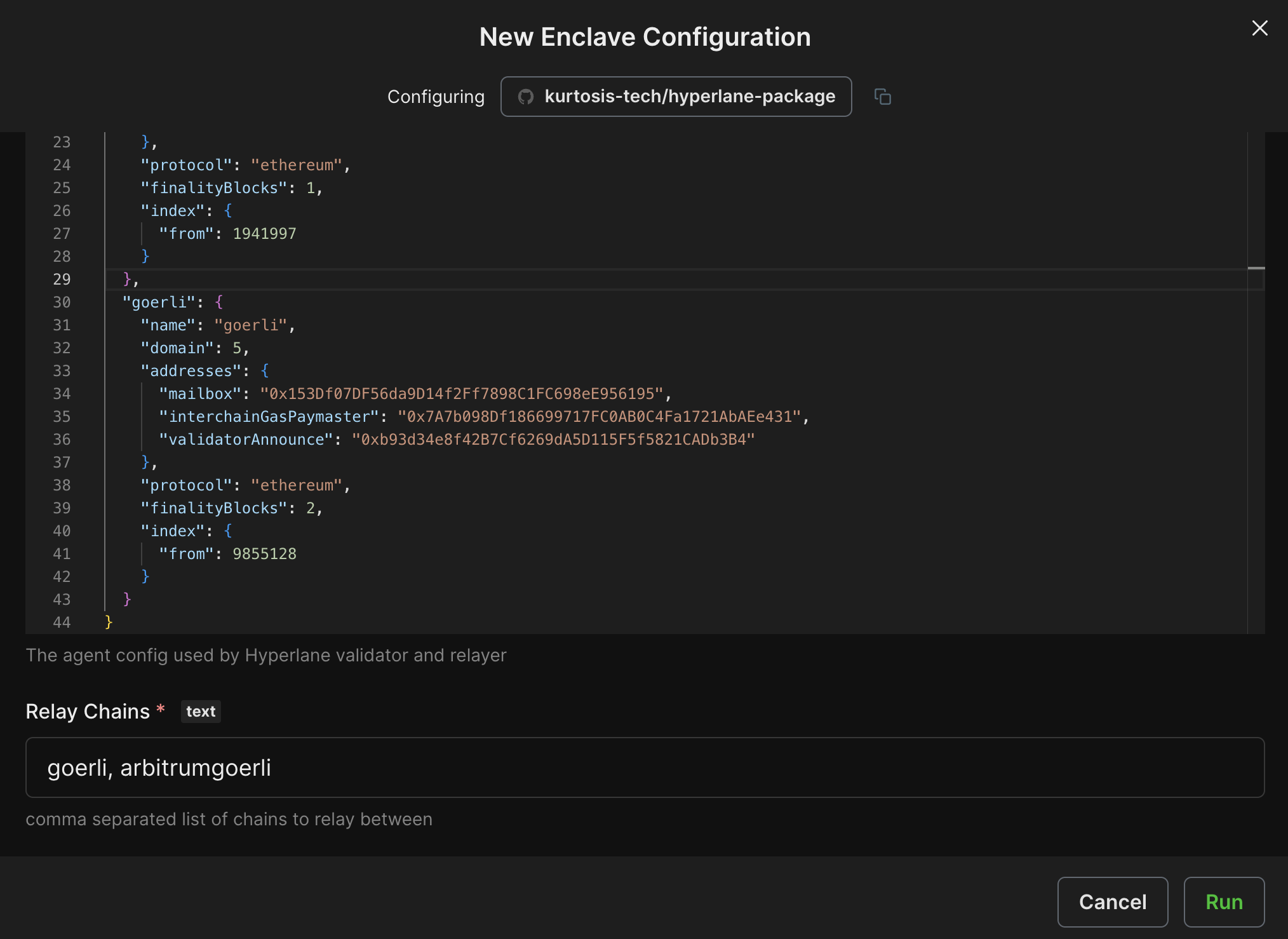
Click Run to deploy your relayer and validator!
Once the configuration finishes executing successfully, you'll see a green check mark. Congratulations! You've now deployed your own relayer and validator with Kurtosis!
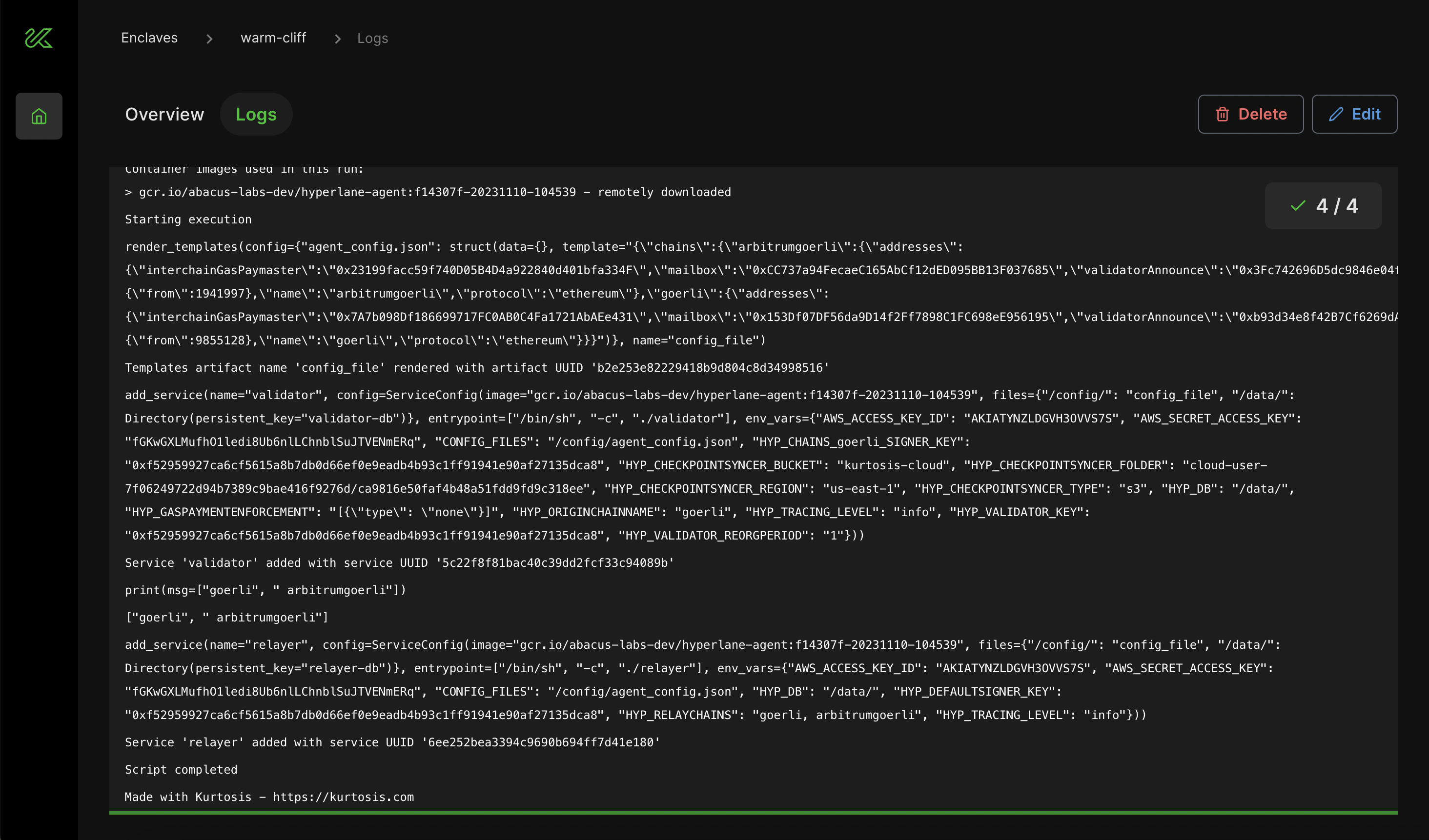
You can see information about your relayer and validator deployment, including logs, by navigating to the Overview tab.
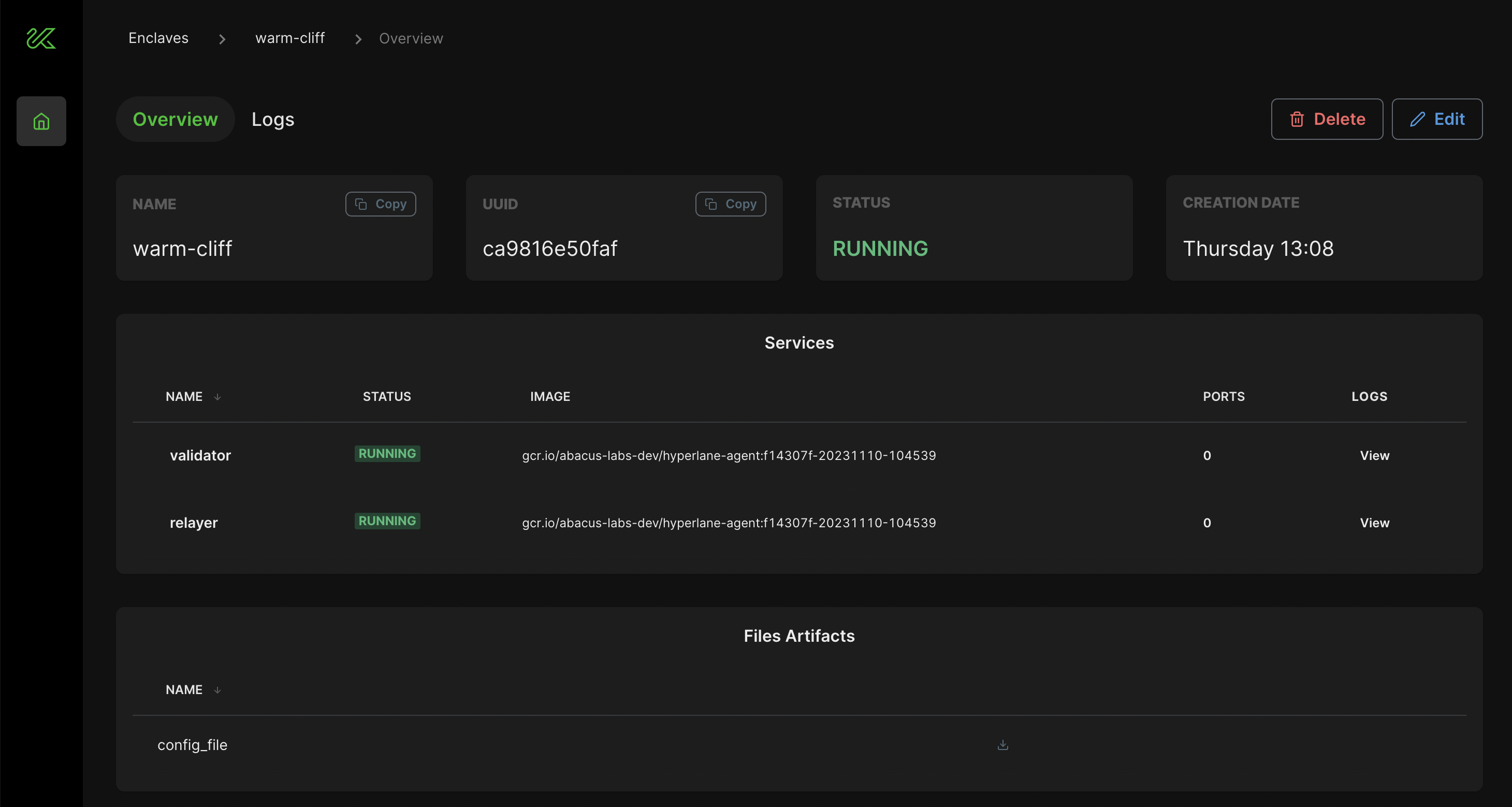
For issues with Kurtosis, please file an issue on the Kurtosis Github repository. For questions or discussion, use the Github Discussions section of the Kurtosis repository or visit the Kurtosis Discord server.
4. Send test messages
You can check everything is working correctly by sending a test message between pairs of chains.
Initiate the message with the CLI. It will ask for a set of core deployment artifacts to use. Select the core-deployments JSON file from Step 2.
hyperlane send message --key $PRIVATE_KEY
The send message command will inform you when the message is dispatched. After a short wait, a confirmation of delivery will be displayed. If the message delivery times out, it is likely that there's an issue with the Validator or Relayer setup in the steps above. To troubleshoot start by looking at the origin chain relayer logs. If you need further help, reach out on Discord.
5. (Optional) Deploy a Warp Route
To connect tokens using your new Hyperlane deployment, see the Warp Route deployment guide.